Understanding Layer 2 Solutions in Crypto: Scaling Beyond the Blockchain
Ever wondered why blockchain hasn't yet become a part of our daily lives despite its potential? Blockchain promises to revolutionize everything from finance to supply chains, but it's facing some serious roadblocks. High transaction fees, slow processing times, and limited scalability are preventing blockchain from reaching its full potential and mass adoption.
How can we overcome these challenges? This is where Layer 2 solutions come in. They are designed to address the limitations of Layer 1 blockchains, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more efficient. So, what are Layer 2 protocols, and why are they the key to the future of blockchain? Let's find out.
Ever wondered why blockchain hasn't yet become a part of our daily lives despite its potential? Blockchain promises to revolutionize everything from finance to supply chains, but it's facing some serious roadblocks. High transaction fees, slow processing times, and limited scalability are preventing blockchain from reaching its full potential and mass adoption.
How can we overcome these challenges? This is where Layer 2 solutions come in. They are designed to address the limitations of Layer 1 blockchains, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more efficient. So, what are Layer 2 protocols, and why are they the key to the future of blockchain? Let's find out.
What is Layer 2 Blockchain?
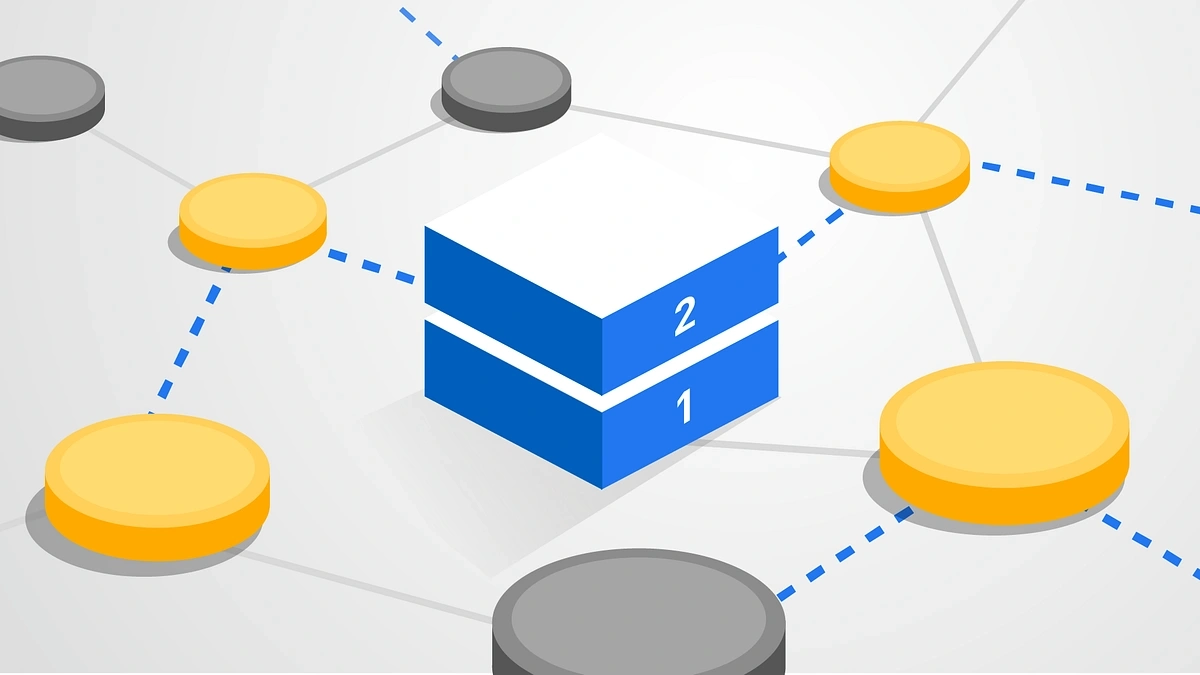
Layer 2 solutions are secondary frameworks or protocols built on top of an existing blockchain system (Layer 1). Think of Layer 1 as the main highway and Layer 2 as additional lanes or even separate roads that help manage traffic more efficiently.
Difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 1, or the main blockchain (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum), handles all core transactions and security. Layer 2 works on top of Layer 1 to enhance its capabilities, especially in terms of speed and scalability, by offloading some tasks from the main chain to improve overall performance.
The Need for Layer 2 Solutions
Blockchain is relatively new, so why do we already need to add to Layer 1 solutions? Well, they face some challenges that need addressing if blockchain is to scale to mass adoption. Layer 1 blockchains can only handle a limited number of transactions per second, leading to network congestion and slow confirmation times.
During peak usage, transaction fees can skyrocket, making it expensive to use the blockchain. However, that’s where L2 protocols come to the rescue.
Scalability Issues
We need Layer 2 scaling technology because popular blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum face congestion as every node must process every transaction, leading to slow and expensive transactions.
High Transaction Costs
When network usage spikes, transaction fees on Layer 1 blockchains can skyrocket. Layer 2 alleviates this by processing transactions off-chain, significantly lowering costs.
Latency
Confirming transactions on Layer 1 can take minutes, which isn't ideal for many applications. Layer 2 solutions provide near-instant transaction confirmations, greatly improving the user experience.
Mass Adoption
For blockchain technology to be widely adopted, it needs to handle millions of transactions per second efficiently and affordably. Layer 2 solutions make this possible by boosting overall transaction capacity.
Interoperability
Layer 2 solutions also help facilitate better interoperability between different blockchains, allowing assets and data to move more freely across various networks.
Greater Privacy
Conducting transactions off-chain with some Layer 2 solutions offers improved privacy, making it harder for outside observers to track activities.
Smart Contract Efficiency
Layer 2 can optimize the execution of smart contracts, making them faster and cheaper to run.
In essence, Layer 2 solutions overcome the limitations of Layer 1 blockchains, making them faster, cheaper, and more practical for everyday use. This is crucial for the broader adoption and usability of blockchain technology.
Importance of Layer 2 for Mass Adoption
For blockchain to go mainstream, it needs to handle a lot more transactions quickly and cheaply. Layer 2 scaling solutions help make this possible. They boost the number of transactions that can be processed at once, cut down on costs, and speed up how fast transactions get confirmed.
Without Layer 2, using blockchain for everyday things like payments, gaming, and decentralized finance (DeFi) would be a headache because of the limitations of Layer 1. Layer 2 makes it feasible for the blockchain to support millions of users and transactions, making the technology accessible and practical for everyone.
How Layer 2s Work
OK, so we’ve established that Layer 1 blockchains are slow and that’s why we need Layer 2. To counteract this, Layer 2 technologies work by taking transactions off the main blockchain (Layer 1) and processing them separately in a more efficient environment.
- Step 1. Off-Chain Processing: Transactions are moved off the main blockchain to be processed. This involves taking the bulk of transaction activity away from Layer 1 to reduce congestion.
- Step 2. Processing Transactions: These transactions are processed in parallel systems, which can handle them much faster and at a lower cost because they don’t need to be validated by every node in the main network.
- Step 3. Anchoring Back to Layer 1: After processing, the results are periodically anchored back to the main blockchain. This means a summary of all the off-chain transactions is recorded on Layer 1, ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain.
This method reduces the workload on Layer 1, making the entire system more efficient while still maintaining the decentralized nature and security of the main blockchain.
Types of Layer 2 Blockchains
State Channels
These allow two parties to transact off-chain, meaning they can make numerous transactions without involving the main blockchain each time. Only the final result of these transactions is broadcast to the blockchain. This significantly reduces congestion and speeds up the process. A popular example is the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, which enables fast, low-cost payments.
Sidechains
These are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main chain and are connected through a two-way peg, which allows assets to be transferred between the main chain and the sidechain. Sidechains can operate independently with their own rules and features, providing flexibility and reducing the load on the main chain.
Examples include the Liquid Network, which enhances Bitcoin's capabilities, and RSK, which adds smart contract functionality to Bitcoin.
Rollups
Rollups batch multiple transactions into a single one and post it to the main chain. They come in two main types: Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups. Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid by default and only run computations if challenged, whereas ZK-Rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to ensure transactions are correct before posting them to the main chain.
Examples include Arbitrum (Optimistic Rollup) and zkSync (ZK-Rollup), both of which help scale Ethereum by increasing throughput and reducing costs.
Plasma
Plasma creates smaller, secondary chains (Plasma chains) that run parallel to the main chain. These chains handle most of the transactional load and periodically submit summaries to the main chain.
Plasma helps scale Ethereum by offloading transactions to these smaller chains, thereby reducing congestion on the main chain. OmiseGO is an example of a project using Plasma to facilitate fast and inexpensive transactions.
Overall Advantages of Layer 2 Chains
- Improved Scalability: Handles more transactions per second, reducing congestion on the main blockchain.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Off-chain processing significantly reduces costs.
- Faster Transaction Times: Enables near-instantaneous confirmations, enhancing user experience.
- Reduced Load on Layer 1: Offloads transactions from the main blockchain, improving overall performance.
- Enhanced Privacy: Offers better privacy by conducting transactions off-chain.
- Better User Experience: Combines faster transactions and lower fees for a more accessible system.
- Interoperability: Facilitates seamless transfer of assets and data across different blockchains.
- Optimized Smart Contracts: Makes executing smart contracts faster and cheaper, benefiting DeFi applications.
What Are the Best Layer 2 Crypto in 2024?
- Arbitrum (ARB)
- Optimism (OP)
- Polygon (MATIC)
- zkSync (ZKS)
- Immutable X (IMX)
- Lightning Network (for Bitcoin)
- Base (Coinbase Layer 2 Network)
- Mantle (MNT)
- Loopring (LRC)
- Coti (COTI)
Layer 2 Blockchain Makes Crypto Easier For The Masses
Overall, L2 blockchain is essential for scaling blockchain technology, making it faster, cheaper, and more accessible for everyday use. They play a crucial role in driving the mass adoption of blockchain by addressing the inherent limitations of Layer 1 systems.Ever wondered why blockchain hasn't yet become a part of our daily lives despite its potential? Blockchain promises to revolutionize everything from finance to supply chains, but it's facing some serious roadblocks. High transaction fees, slow processing times, and limited scalability are preventing blockchain from reaching its full potential and mass adoption.
How can we overcome these challenges? This is where Layer 2 solutions come in. They are designed to address the limitations of Layer 1 blockchains, making transactions faster, cheaper, and more efficient. So, what are Layer 2 protocols, and why are they the key to the future of blockchain? Let's find out.
What is Layer 2 Blockchain?
Layer 2 solutions are secondary frameworks or protocols built on top of an existing blockchain system (Layer 1). Think of Layer 1 as the main highway and Layer 2 as additional lanes or even separate roads that help manage traffic more efficiently.
Difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 Solutions
Layer 1, or the main blockchain (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum), handles all core transactions and security. Layer 2 works on top of Layer 1 to enhance its capabilities, especially in terms of speed and scalability, by offloading some tasks from the main chain to improve overall performance.
The Need for Layer 2 Solutions
Blockchain is relatively new, so why do we already need to add to Layer 1 solutions? Well, they face some challenges that need addressing if blockchain is to scale to mass adoption. Layer 1 blockchains can only handle a limited number of transactions per second, leading to network congestion and slow confirmation times.
During peak usage, transaction fees can skyrocket, making it expensive to use the blockchain. However, that’s where L2 protocols come to the rescue.
Scalability Issues
We need Layer 2 scaling technology because popular blockchain platforms like Bitcoin and Ethereum face congestion as every node must process every transaction, leading to slow and expensive transactions.
High Transaction Costs
When network usage spikes, transaction fees on Layer 1 blockchains can skyrocket. Layer 2 alleviates this by processing transactions off-chain, significantly lowering costs.
Latency
Confirming transactions on Layer 1 can take minutes, which isn't ideal for many applications. Layer 2 solutions provide near-instant transaction confirmations, greatly improving the user experience.
Mass Adoption
For blockchain technology to be widely adopted, it needs to handle millions of transactions per second efficiently and affordably. Layer 2 solutions make this possible by boosting overall transaction capacity.
Interoperability
Layer 2 solutions also help facilitate better interoperability between different blockchains, allowing assets and data to move more freely across various networks.
Greater Privacy
Conducting transactions off-chain with some Layer 2 solutions offers improved privacy, making it harder for outside observers to track activities.
Smart Contract Efficiency
Layer 2 can optimize the execution of smart contracts, making them faster and cheaper to run.
In essence, Layer 2 solutions overcome the limitations of Layer 1 blockchains, making them faster, cheaper, and more practical for everyday use. This is crucial for the broader adoption and usability of blockchain technology.
Importance of Layer 2 for Mass Adoption
For blockchain to go mainstream, it needs to handle a lot more transactions quickly and cheaply. Layer 2 scaling solutions help make this possible. They boost the number of transactions that can be processed at once, cut down on costs, and speed up how fast transactions get confirmed.
Without Layer 2, using blockchain for everyday things like payments, gaming, and decentralized finance (DeFi) would be a headache because of the limitations of Layer 1. Layer 2 makes it feasible for the blockchain to support millions of users and transactions, making the technology accessible and practical for everyone.
How Layer 2s Work
OK, so we’ve established that Layer 1 blockchains are slow and that’s why we need Layer 2. To counteract this, Layer 2 technologies work by taking transactions off the main blockchain (Layer 1) and processing them separately in a more efficient environment.
- Step 1. Off-Chain Processing: Transactions are moved off the main blockchain to be processed. This involves taking the bulk of transaction activity away from Layer 1 to reduce congestion.
- Step 2. Processing Transactions: These transactions are processed in parallel systems, which can handle them much faster and at a lower cost because they don’t need to be validated by every node in the main network.
- Step 3. Anchoring Back to Layer 1: After processing, the results are periodically anchored back to the main blockchain. This means a summary of all the off-chain transactions is recorded on Layer 1, ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain.
This method reduces the workload on Layer 1, making the entire system more efficient while still maintaining the decentralized nature and security of the main blockchain.
Types of Layer 2 Blockchains
State Channels
These allow two parties to transact off-chain, meaning they can make numerous transactions without involving the main blockchain each time. Only the final result of these transactions is broadcast to the blockchain. This significantly reduces congestion and speeds up the process. A popular example is the Lightning Network for Bitcoin, which enables fast, low-cost payments.
Sidechains
These are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main chain and are connected through a two-way peg, which allows assets to be transferred between the main chain and the sidechain. Sidechains can operate independently with their own rules and features, providing flexibility and reducing the load on the main chain.
Examples include the Liquid Network, which enhances Bitcoin's capabilities, and RSK, which adds smart contract functionality to Bitcoin.
Rollups
Rollups batch multiple transactions into a single one and post it to the main chain. They come in two main types: Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups. Optimistic Rollups assume transactions are valid by default and only run computations if challenged, whereas ZK-Rollups use zero-knowledge proofs to ensure transactions are correct before posting them to the main chain.
Examples include Arbitrum (Optimistic Rollup) and zkSync (ZK-Rollup), both of which help scale Ethereum by increasing throughput and reducing costs.
Plasma
Plasma creates smaller, secondary chains (Plasma chains) that run parallel to the main chain. These chains handle most of the transactional load and periodically submit summaries to the main chain.
Plasma helps scale Ethereum by offloading transactions to these smaller chains, thereby reducing congestion on the main chain. OmiseGO is an example of a project using Plasma to facilitate fast and inexpensive transactions.
Overall Advantages of Layer 2 Chains
- Improved Scalability: Handles more transactions per second, reducing congestion on the main blockchain.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Off-chain processing significantly reduces costs.
- Faster Transaction Times: Enables near-instantaneous confirmations, enhancing user experience.
- Reduced Load on Layer 1: Offloads transactions from the main blockchain, improving overall performance.
- Enhanced Privacy: Offers better privacy by conducting transactions off-chain.
- Better User Experience: Combines faster transactions and lower fees for a more accessible system.
- Interoperability: Facilitates seamless transfer of assets and data across different blockchains.
- Optimized Smart Contracts: Makes executing smart contracts faster and cheaper, benefiting DeFi applications.
What Are the Best Layer 2 Crypto in 2024?
- Arbitrum (ARB)
- Optimism (OP)
- Polygon (MATIC)
- zkSync (ZKS)
- Immutable X (IMX)
- Lightning Network (for Bitcoin)
- Base (Coinbase Layer 2 Network)
- Mantle (MNT)
- Loopring (LRC)
- Coti (COTI)
Layer 2 Blockchain Makes Crypto Easier For The Masses
Overall, L2 blockchain is essential for scaling blockchain technology, making it faster, cheaper, and more accessible for everyday use. They play a crucial role in driving the mass adoption of blockchain by addressing the inherent limitations of Layer 1 systems.